IA
Informační architektura
Information architecture
Lukáš Bařinka
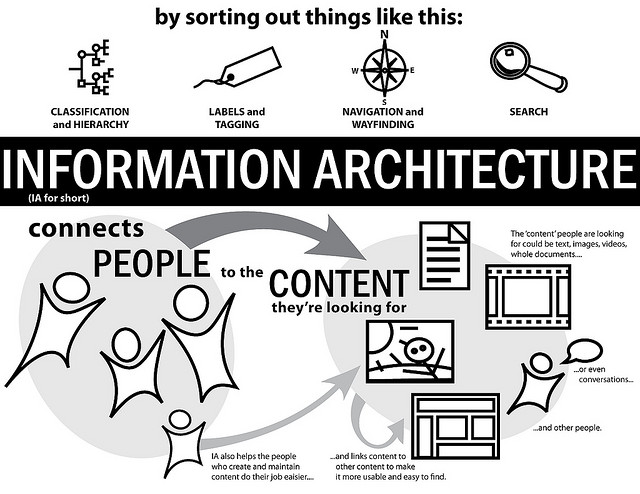
Information architecture (IA) is the art and science of
organizing and labelling data
including: websites, intranets, online communities and
software to support usability.
Informační architektura (IA) je umění a věda zabývající se
organizací a označováním (pojmenováním) dat
zahrnující: weby, intranety, online comunity a
software podporující použitelnost.
Table of contentsObsah
What is IACo je IA
- The structural design of shared information environments.
- The combination of organization, labeling, search and navigation systems within websites and intranets.
- The art and science of organizing and labeling web sites, intranets, online communities, and software to support findability and usability.
- An emerging community of practice focused on bringing principles of design and architecture to the digital landscape.
- Strukturální návrh prostředí sdílených informací.
- Kombinace systémů organizace, označování, vyhledávání a navigace na webových stránkách a intranetech.
- Umění a věda organizování a označování webových stránek, intranetů, online komunit a softwaru na podporu vyhledatelnosti a použitelnosti.
- Vznikající komunita praktik zaměřená na přinášení principů designu a architektury do digitální krajiny.
Rosenfeld, Louis; Morville, Peter:
Information architecture for the World Wide Web
Why IAProč IA
- The cost of finding information
- The cost of not finding information
- The value of education
- The cost of construction
- The cost of maintenance
- The cost of training
- The value of brand
- Cena nalezení informace
- Cena nenalezení informace
- Cena vzdělání
- Cena vytvoření/změny
- Cena údržby
- Hodnota zaškolení
- Hodnota značky (firmy)
OverviewPřehled
Information EcologyProstředí IA
- Understand the business goals behind the web site and the resources available for design and implementation
- Be aware of the nature and volume of content that exists today and how that might change a year from now
- Learn about the needs and information-seeking behaviors of our users
- Chápat obchodní cíle, technologie, procesy, rozpočet, omezení webu
- Uvědomovat si povahu, množství, strukturu, formát a dynamiku obsahu a metadat
- Poznávat potřeby a způsoby chování a vyhledávání, zkušenosti uživatelů
Needs of Information SeekingPotřeby hledání informací
- Perfect catch Looking for the right answer
- Lobster trapping Looking for more than just a single answer
- Indiscriminate driftnetting Leave no stone unturned
- I've seen you before, Mobydick… Never lose track - so you can find it again
- Trefa do černého (Perfect catch) Hledání přesné odpovědi
- Každá informace dobrá (Lobster trapping) Hledání více než jen odpovědi (je to ta správná?)
- Co je doma, to se počítá (Indiscriminate driftnetting) Hledání všech dostupných informací
- To už jsem někde viděl (I've seen you before, Mobydick) Znovunalezitelná informace
IA ComponentsČásti IA
- Organization Systems Organize to understand, to explain, and to control
- Labeling Systems (labeling) Way to clearly show the user your organization and navigation systems
- Navigation Systems Getting lost in a large web site can be confusing and frustrating
- Search Systems Another form of finding information
- Organizace Kategorizace, časové řazení, ...
- Značení (labeling) Způsob reprezentace informací, ...
- Navigace Procházení informacemi, průchod hierarchií, ...
- Vyhledávání Indexace a dotazování, ...
Organization systemsZpůsoby organizace
What to organizeCo organizovat
- Headings Labels for the content that follows them
- Embedded links Label the content they link to
- Embedded metadata Must first be extracted
- Chunks Logical units of content - e.g., sections and chapters are both chunks
- Lists Grouped together, particular order
- Sequential aids Where the user is in a process or task, and how far he has to go
- Identifiers Where the user is in an information system, e.g., a logo, or a breadcrumb
- Nadpisy Označení následujícího obsahu
- Odkazy v textu Reprezentace obsahu cíle
- Obsažená metadata Musí být nejdříve zpracována
- Kusy obsahu Logické jednotky - kapitoly, jejich struktura
- Seznamy Souvislost, pořadí
- Pořadí kroků procesuV jaké části procesu se uživatel nachází a co ještě zbývá
- Identifikátory Určení polohy v informačním systému, logo, drobečková navigace
ProblemsProblémy
- Ambiguity Words are capable of being understood more than one way
- Heterogeneity Object or collection of objects composed of unrelated or unlike parts
- Differences in Perspectives E.g., the ways people organize and name files and directories
- Internal Politics Make compromises to avoid serious political conflict
- Nejednoznačnost jazyka Slova mohou mít více významů, lze je chápat různě
- Heterogenita (informace) Předmět nebo skupina předmětů složené z nesouvisejících nebo nesourodých částí
- Rozdílné pohledy Např. rozdílné způsoby, jakými lidé uspořádávají soubory a adresáře
- Vnitřní politika Kompromisy mezi různými „politickými“ zájmy
Exact organization schemePřesná (objektivní) organizace
- Mutualy exclusive
- Must know what you're looking for
- Easy to use
- Výlučná
- Potřeba vědět co hledat
- Jednoduché použití
ExamplesPříklady
- Alphabetical Encyclopedias and dictionaries
- Chronological Archive, history books, magazine archives, diaries, and television guides
- Geographical Maps, regions
- Abecední Encyklopedie, adresáře
- Chronologická Archivy, novinky, ročenky, historické knihy, diáře, televizní programy
- Geografická Mapy, regiony
Ambiguous organization schemeNejednoznačná (subjektivní) organizace
- Non-exclusive
- Don't always know what we're looking for
- Often iterative and interactive
- Depends on schema quality and careful item placing, scheme changes, user-testing
- Nevýlučná
- Není potřeba přesně znát hledané označení
- Iterativní, interaktivní
- Záleží na kvalitě schématu a pečlivém umístění položek, změny schématu, uživatelské testování
ExamplesPříklady
- Topic
- Task Processes, functions, or tasks, task-oriented menus
- Audience Open or closed
- Metaphor Understand the new by relating it to the familiar)
- Hybrids
- Podle témat
- Podle úkolů Procesy, funkce, úkoly, submenu akcí
- Podle rolí Otevřená/uzavřená
- Podle podobností Metafor, reálného světa
- Hybridní
Hierarchical organization structureHierarchická organizace
- A Top-Down Approach
- Mutually exclusive subdivisions
- Parent-child relationships
- If too many items are cross-listed, the hierarchy loses its value
- Important to consider the balance between breadth and depth
- Přístup shora-dolů
- Výlučné podčásti (jinak polyhierarchie)
- Vztahy rodič-potomek
- Uvedení prvku v mnoha kategoriích může hierarchii znehodnotit
- Nezbytné vyvážení šířky a hloubky struktury
Database Organization StructureDatabázová organizace
- A Bottom-Up Approach
- Built upon the relational database model
- Automatic generation of alphabetical indexes
- Dynamic presentation of associative "see also" links
- Fielded searching
- Advanced filtering and sorting of search results
- Zdola-nahoru
- Založeno na relačních metadatech
- Automaticky generované (lexikografické) indexy
- Dynamicky zobrazované příbuzné informace (see also)
- Vyhledávání podle kritérií
- Pokročilé filtrovaní a řazení výsledků
Hypertext organization structureHypertextová organizace
- Nonlinear way of structuring information
- Great flexibility
- Can't simply create a mental model of the site organization
- Easy to get lost
- Nelineární strukturování informací
- Velmi flexibilní
- Problematické vytvoření mentálního modelu
- Snadná ztráta orientace
Cohesive organization systemsSoudržné (koherentní) systémy organizace
- Distinction between exact and ambiguous schemes
- Providing multiple ways to access the same information
- Break down the site into its components
- Collections of structured, homogeneous information
- Používat (přesnou) objektivní i (nejednoznačnou) subjektivní organizaci
- Poskytovat více cest k informacím
- Rozdělení složité oblasti na části (komponenty)
- Nejlepší výsledky při použití úzkých domén homogenního obsahu
LabelingZnačení (Labeling)
Labeling SystemsSystémy značení (labeling)
- Form of simple (one-word) representation of larger chunks of information
- Shortcut that triggers the right association in the user's mind (e.g., "Contact Us")
- Goal is to communicate efficiently; to convey meaning without taking up too much space (vertical and/or cognitive)
- Most obvious way to clearly show the user your organization and navigation systems
- Forma zjednodušené (jednoslovné) reprezentace většího množství informací
- Zkratka reprezentující obsah (např. kontakty)
- Cílem je efektivní komunikace nezabírající příliš mnoho prostoru (webové stránky nebo pozornosti uživatele)
- Nejjasnější způsob, jak ukázat uživateli organizační a navigační systém
Common Labeling ProblemsČasté problémy značení
- The labels aren't representative
- The labels don't differentiate
- The labels are jargony
- The labels are not user-centric
- The labels waste money Any time an architecture intrudes on a user's experience, he may give up on a site and go somewhere else
- The labels don't make a good impression The words you use can make or break your business deals
- Označení není reprezentativní Nevystihuje podstatu věci
- Označení nerozlišuje Není zřejmé čím se označení liší
- V označení se používá žargon
- Označení není zaměřené na uživatele Např. předpokládá znalosti profesionála nebo zaměstnance)
- Označení zavádí uživatele, který následně odchází Uživatel se ztrácí nebo neví, co zvolit
- Označení nevytváří dobrý dojem Neprofesionální označení, nedůvěryhodné
Varieties of LabelTypy značení
- Contextual links
- Headings
- Navigation system choices
- Index terms
- Iconic Labels
- Kontextové odkazy
- Nadpisy
- Položky navigace
- Pojmy v indexu (rejstřík)
- Ikony
Contextual LinksKontextové odkazy
- Meaning from its surrounding text
- Explanatory text, clear headings
- May mean different things to different people
- Created in an ad hoc manner
- Usually, content authors are responsible for contextual links
- Kontext okolního textu
- Samovysvětlující obsah
- Různé očekávání u příliš jednoduchých odkazů (např. jedno slovo, jméno)
- Nekonzistence použití (ad hoc)
- Použití v kompetenci autora (doporučení pro autory)
HeadingsNadpisy
- Describe the chunk of information that follows
- Hierarchical relationships usually established visually
- Set of labels that don't mean much can suddenly take on meaning when presented in a hierarchy
- Označení následujícího textu
- Obvykle vizuální rozlišení úrovně nadpisu
- Označení pořadí usnadňuje orientaci a pochopení struktury (kontext v hierarchii)
Items in navigationPoložky navigace
- Demand consistent application more than any other type of label
- Inconsistent option can introduce an "apples and oranges" effect very quickly
- Common variants
- Main (Page), Home
- Search, Find, Browse
- Site Map, Contents, TOC, Index
- Contact (Us)
- Help, FAQ, Q&A
- News (& Events)
- About (Us), Who We Are
- Případné problémy mají obvykle širší dopad (celý web)
- Neměnný obsah a význam
- Obvyklé (ustálené) označení
- Main (Page), Home
- Search, Find, Browse
- Site Map, Contents, TOC, Index
- Contact (Us)
- Help, FAQ, Q&A
- News (& Events)
- About (Us), Who We Are
Index termsIndex (rejstřík)
- Keywords, tags, descriptive metadata, taxonomies, controlled vocabularies, and thesauri, sets of index term labels
- More precise searching Than simply searching the full text
- Completely (usually) invisible to users
- Klíčová slova (keywords), značky (tag), popis (description), taxonomie, řízené slovníky, lexikony
- Slouží pro preciznější vyhledávání Lepší než prosté full-text vyhledávání
- Obvykle neviditelné pro uživatele
IconsIkony
- Most frequently used as navigation system labels
- Much more limited language than text
- Work well for less text-oriented audiences
- Useful shorthand
- Add aesthetic quality to a site
- Obvykle v navigaci
- Omezenější jazyk než u textu
- Snadnější komunikace, pokud text selhává (jazykové bariéry, vzdělání)
- Zrychluje použití navigace
- Přidává estetický prvek
Designing LabelsDoporučení pro výběr označení
- Narrow scope whenever possible
(context, content, user) - Consistent labeling systems, not labels
- Style And or &, punctuation, proofreader
- Presentation Application of fonts, font sizes, colors, whitespace, and grouping
- Syntax E.g., verb-based XOR noun-based XOR question-based labels
- Granularity Labels that are roughly equal in their specificity
- Comprehensiveness No noticeable gaps in a labeling system
- Audience Languages of your site's major audiences
- Co nejuzší doména (context, content, user)
- Konzistentní, předvídatelný systém označení
- Styl A/&, interpunkce
- Vizuální reprezentace Barva, font, velikost, seskupování
- Syntaxe Např. podstatná jména, styl otázek
- Granularita Stejná úroveň pro společné prvky
- Kompletní obsah Neopomenout něco
- Uživatelsky zaměřený Vhodně zvolený jazyk
NavigationNavigace
Types of Navigation SystemsZákladní typy
- Global Where Am I?
- Local What's Nearby?
- Contextual What's Related to What's Here?
- Supplemental Sitemap, Index, Guide
- History In Browser
- Globální Kde jsem?
- Lokální Co je poblíž?
- Kontextová Co s tím souvisí?
- Doplňková Sitemap, index, průvodci
- Historie V prohlížeči
Global (site-wide)Globální
- Often horizontal
- Leading to a Home Page
- Contains Search element
- Highlights current position
- Často horizontální
- S odkazem na hlavní stránku
- S prvkem pro vyhledávání
- Vyznačená současná poloha
LocalLokální
- Completing global navigation systems
- Often vertical
- Explore the immediate area
- Often multiple local navigation systems
- Doplňující globální navigaci
- Často vertikální
- Odkazy na podstránky
- Mnohdy vícečetná (různé přístupy - organizace)
ContextualKontextová
- More editorial than architectural
- Sometimes automatically generated
- Link content and context matches the meaning
- Usually related products or topics
- Provide a specific area of the page or a visual convention
- Obvykle v režii autora než architekta
- Občas strojově generovaná
- Obsah odkazu i jeho kontext vypovídá o cíli
- Obvykle na produkty nebo související obsah
- Vhodné umístnění a vzhled
Implementing embedded navigationImplementace navigace
- Global, local, and contextual navigation elements exist together on most pages
- Together they monopolize a great deal of screen real estate
- Textual labels versus icons
- Distinct collection of hypertext links
- Placing: global along the top, local along the left side
- Beware of accessibility and usability
- Navigace zabírá významný díl plochy stránky
- Flexibilita navigace Vs zmatení uživatele
- Navigace (lokální a globální) je v podstatě seznam hypertextových odkazů
- Technická implementace pomocí textů, obrázků, menu a tlačítek (form), kaskáda menu (list, form), pop-up (CSS/JS), rámy, XML
- Umístění (globální nahoru, lokální doleva)
- Pozor na přístupnost a použitelnost
SitemapMapa stránek
- Presents the top few levels of the information hierarchy
- Graphical or text-based links
- Broad view of the content in the web site
- Provide the user with direct access to pages of the site
- Useful from a search engine optimization perspective
- Snadná pro hierarchickou organizaci
- Několik (všechny) nejvyšších úrovní hierarchie
- Textová nebo grafická podoba
- Slouží uživateli k rozkrytí organizační struktury
(ne k vyděšení z rozsáhlosti) - Umožňuje rychlý řístup k jednotlivým částem
- Slouží pro vyhledávače
Site IndexesIndexy
- Keywords or phrases alphabetically
- Without representing the hierarchy Relatively flat
- Level of granularity Pages, paragraphs or concepts…?
- Know your audience and understand their needs Search analyzing
- Create the index manually/dynamically
- Term rotation AKA permutation Both "refund, IRS" and "IRS refund"
- Klíčová slova a sousloví v abecením pořadí
- Neobsahuje hierarchii (lineární)
- Úroveň detailu Granularita - stránka, kapitola, odstavec, …
- Respektování potřeb uživatelů Analýza logů vyhledávání
- Ruční konstrukce, automatické generování
- Rotace (permutace) sousloví Formulář, daň z příjmu / daň z příjmu, formulář / přiznání k dani z příjmu
GuidesPrůvodci (guides)
- Forms: guided tours, tutorials, and micro-portals
- Introducing users to the content and functionality
- The guide should be short
- At any point, the user should be able to exit the guide
- Navigation (Previous, Home, Next)
- Designed to answer questions
- Screenshots with enlarged details of key features
- Own table of contents (if more than a few pages)
- Typy: prohlídky, tutoriály, mikroportály
- Obvykle nehrají hlavní roli při návštěvě webu
- Krátké, kdykoli opustitelné
- Konzistentní umístění navigace (zpět/dopředu/start/opustit)
- Záměrem průvodce je odpovídat na (potenciální) dotazy
- Použití screenshotů (se zvětšenými detaily)
- Obsah (TOC) pro průvodce delší než několik stránek
Wizards and ConfiguratorsPomocníci a konfigurátory (wizards)
- Special class of guide
- Helps users to configure products or navigate complex decision trees
- Blurs the lines between software application and web site
- Users move through a linear process or jump back and forth between steps
- Providing context and possible next steps
- Speciální případ průvodců
- Konfigurace produktů
- Smazává rozdíl mezi webovou stránkou a aplikací
- Umožnit přeskočit některou část nebo se vrátit
- Zobrazovat kontext kroků
SearchVyhledávání
- Tremendous level of specificity
- Unlikely to be represented in a sitemap or site index
- Favorite tool of users because it puts them in the driver's seat
- Ambiguity of language causes huge problems
- Variabilita úrovně detailu
- Netřeba se trefovat do pojmů v indexu
- Potenciálně rychle vedoucí k cíli (při správných dotazech)
- Problém s nejednoznačností jazyka
Advanced Navigation ApproachesPokročilé principy navigace
- Personalization
- Customization
- Visualization
- Social Navigation
- Personalizace
- Přizpůsobování (customization)
- Vizualizace
- Sociální navigace
PersonalizationPerzonalizace
- Based upon a model of the behavior, needs, or preferences of the individual user
- We guess what the user wants from statistics, history (history doesn't guarantee the future)
- Na základě chování, potřeb, preferencí, … uživatele
- pouze odhad, statistiky, historie (historie nezaručuje budoucnost), uživatelské role
CustomizationPřizpůsobování (customization)
- Direct control over some combination of presentation, navigation, and content options
- User tells us what s/he wants
- Most people don't want to spend much (if any) time customizing
- Users themselves don't always know what they will want to know or do tomorrow
- E.g.: OECD Better Life Index
- Řízení prezentace, navigace a obsahu uživatelem
- Na základě požadavků uživatele
- Neochota uživatelů nastavovat (např. pro jednu návštěvu)
- Problematické přispůsobování při nerutinních akcích
- Např.: OECD Better Life Index
VisualizationVizualizace
- Using physical metaphors (library, museum) and abstracts (graphs)
- Does not prove to be used globally
- Examples
- Přitažlivá a zajímavá
- Použití metafor (knihovna, obchod) a abstrakcí (grafy, množiny)
- Obtížně použitelná globálně
- Příklady
Social NavigationSociální navigace
- Recommendations (most popular, also bought)
- Tag clouds
- Search logs, usage statistics, and customer databases
- E.g.: Pinterest ideas
- Spolupráce při filtrování
- Doporučení (nakoupili také)
- Tag clouds
- Logy vyhledávání a statistiky
- Např.: Pinterest ideas
SearchVyhledávání
Does Your Site Need Search?Je vyhledávání potřeba?
- Does your site have enough content?
- Will investing in search systems divert resources from more useful navigation systems?
- Do you have the time and know-how to optimize your site's search system?
- Are there better alternatives?
- Will your site's users bother with search?
- Je pro vyhledávání dostatek (podle typu) obsahu?
- Neodčerpá implementace vyhledávání zroje na jiné druhy navigace?
- Máte čas a znalosti pro optimalizaci vyhledávání?
- Existují lepší alternativy než vyhledávání?
- Budou uživatelé vyhledávat nebo procházet informace?
When to implement search systemsKdy je vhodné vyhledávání
- Search helps when you have too much information to browse
- Search helps fragmented sites
- Search is a learning tool
- Search should be there because users expect it to be there
- Search can tame (slow down) dynamism
- Informací je příliš pro procházení (Yahoo, Seznam)
- Příliš fragmentovaný web bez podpory procházení (Wikipedia)
- Vyhledávání jako nástroj výzkumu potřeb uživatelů
- Uživatelé to očekávají
- Pro zkrocení dynamiky obsahu (velké množství přibývajících informací)
Search System AnatomyProces vyhledávání
Users will ask, browse or search again until they give up.
Uživatelé se budou ptát a procházet výsledky a znova se ptát, dokud to nevzdají.
- User query
- Search interface
- Query language
- Query builders
- Search engine
- Content
- Metadata
- Controlled vocabulary
- Results (SERP)
- Ranking and clustering
- Interface design
- Dotaz uživatele
- Rozhraní pro vyhledávání
- Dotazovací jazyk
- Konstrukce dotazů
- (Webový) vyhledávač
- Obsah
- Metadata
- Řízené slovníky
- Výsledky vyhledávání (SERP)
- Ohodnocení a shlukování
- Návrh rozhraní
What to searchCo hledat
- Full text indexing Doesn't always serve users well
- Search zonespockets of more homogeneous content According to organizational structure, content type, user role, topic, time, author, company division
- Content components Sometimes index autors, sometimes not - copyright, menu)
- Content quality-based search
- Fulltextové vyhledávání Jednoduché nasazení a použití, málo precizní výsledky
- Oblasti zájmu pro vyhledávání (např. ve zboží, kontaktech), obvykle až na další pokus Podle organizační struktury, typu obsahu, typu/role/polohy uživatele, tématu, času, autora, oddělení (firmy)
- Části obsahu V některých vyhledávat - autor, v některých ne - copyright, menu
- Preference vyhledávání obsahu podle jeho kvality
How to searchJak hledat
- Search Algorithms
- Pattern-Matching Algorithms
- Automatic stemming Which expands a term to include other terms that share the same root (or stem)
- Specialized search cited by, active bibliography, similar documents based on text, related documents from co-citation
- Query Builders
- Spell-checkers
- Phonetic tools E.g., "Soundex"
- Stemming tools
- Natural language processing tools E.g., "how to" or "who is"
- Controlled vocabularies and thesauri E.g., synonyms
- Vyhledávací algoritmy
- Shoda podle vzoru Pattern matching
- Hledání podle odvozených slov (stemming) Podle shodného kořene slova
- Specializované vyhledávání podle vztahů Podle citací, autora, podobných dokumentů
- Sestavování dotazů
- Kontrola překlepů
- Fonetické nástroje Např. soundex
- Odvozená slova (stemming)
- Nástroje zpracování přirozeného jazyka how to, who is, …
- Řízené slovníky a lexikony Např. pro synonyma
Search Engine Result Page (SERP)Stránka výsledků vyhledávání
- Which Content Components to Display
- How Many Documents to Display
- Listing Results
- Grouping Results
- Exporting Results
- Které informace zobrazit
- Kolik výsledků zobrazit
- V jakém pořadí zobrazit výsledky
- V jakých skupinách zobrazit výsledky
- Co s nalezenými výsledky
Which Content Components to DisplayKteré informace zobrazit
- Less information to users who know what they're looking for E.g. title
- More information to users who aren't sure what they want E.g. description
- The less results, the more information you might display
- Depends on which components are available in each document E.g. telephone numbers, e-mail
- Méně informací znalým uživatelům Např. titulek
- Více informací neznalým uživatelům Např. popis
- Nepřímá úměra mezi množstvím informací a počtem výsledků
- Podle informací dostupných v cílovém dokumentu Např. telefon, e-mail
How Many Documents to DisplayKolik výsledků zobrazit
- The more information for each retrieved document, the smaller retrieval set, and vice versa
- Affected by a user's monitor resolution, connectivity speed, and browser settings
- Let users know the total number of retrieved documents
- Provide results navigation system
- Nepřímá úměra mezi množstvím informací a počtem výsledků
- Podle potřeby a možností uživatele Např. mobilní verze
- Stránkování výsledků
- Celkový přehled o počtu nalezených výsledků
Listing ResultsV jakém pořadí zobrazit výsledky
- Sorting by alphabet
- Sorting by chronology
- Ranking by relevance Terms count, frequency, distance, importance, popularity
- Ranking by popularity (PageRank)
- Ranking by users' or experts' ratings
- Ranking by pay-for-placement
- Podle abecedy Exikograficky
- Podle času Chronologicky
- Podle relevance Počet výskytů/umístění/příbuznosti obsahu, ceny, vzdálenosti
- Podle popularity PageRank
- Podle názoru uživatelů/expertů
- Podle odměny Pay-for-placement
Grouping ResultsV jakých skupinách zobrazit výsledky
- Generated metadata
- document type E.g. .doc, .pdf
- file creation/modification date
- Manually applied metadata
- topic
- audience SOHO, profi
- language
- product family DLSR, compact, sport cameras
- Generovaná metadata
- Podle typu dokumentu
- Podle času vytvoření/editace
- Ručně vložená metadata
- Podle tématu
- Podle typu uživatelů SOHO, profi
- Podle jazyka
- Podle kategorie produktů DLSR, kompakt, sportovní
Exporting ResultsCo s nalezenými výsledky
- Save and/or modify a search query Not results - to search again later
- Printing, emailing, sharing, or saving results E.g. see later on YouTube, export results (playlist)
- Select a subset of results "Shop" for documents just like shop books at Amazon
- Uložit nebo upravit dotaz a nebo znova hledat Nikoli výsledky, na pozdější hledání
- Vytisknout, odeslat, sdílet, uložit výsledky Např. YouTube - Přehrát později, exportovat výsledky (playlist)
- Vybrat část výsledků Paralela k nákupnímu vozíku, např. vyhledávání podle nalezeného obrázku
Social ClassificationSociální klasifikace